
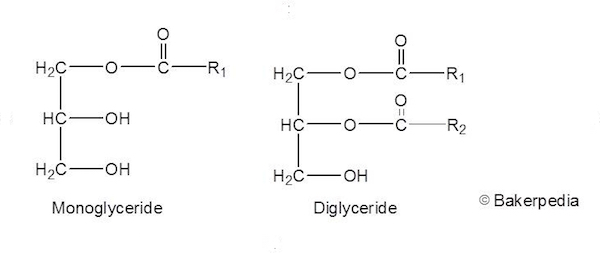
Based on the approach described in the conceptual framework for the risk assessment of certain food additives re-evaluated under Commission Regulation (EU) No 257/2010 and taking into account the considerations mentioned above, the Panel concluded that there was no need for a numerical acceptable daily intake (ADI) and that the food additive mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids (E 471) was of no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels. The Panel noted that the contribution of E 471 represented at the mean only 0.8–3.5% of the recommended daily fat intake. The refined estimates were based on 31 out of 84 food categories in which E 471 is authorised. Gastric infusion of lutein suspended in MDG (20 mg/kg) significantly improved (71-211, P < 0.05) lymphatic lutein output 2-6 h after lipid feeding vs. The available studies did not raise any concern with regard to genotoxicity. Study 2 randomized five groups of lymph fistula rats ( n 4-9/group) to receive 20 mg/kg lutein from either lutein in SO or lutein in four different mono- and diglyceride oils (MDGs). Neither carcinogenic potential nor a promotion effect in initiation/promotion was reported. No evidence for adverse effects was reported in short-term, subchronic studies, chronic, reproductive and developmental toxicity studies. The products are further purified to obtain a mixture of glycerides, free. Mono- and diglycerides are manufactured by the reaction of glycerin with fatty acids or the reaction of glycerin with triglycerides in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. Toxicological studies with mono- and di-glycerides rich in unsaturated fatty acids were considered for the re-evaluation of E 471. The most prevalent fatty acids include lauric, linoleic, myristic, oleic, palmitic, and stearic. Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E471) refers to a naturally occurring class of food additive composed of diglycerides and monoglycerides which is. Glycerol (E 422) and fatty acids (E 570) have been re-evaluated and the Panel concluded that there was no safety concern regarding their use as food additives. The Panel considered that it is very likely that hydrolysis of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids by lipases in the gastrointestinal tract would occur, resulting in the release of glycerol and fatty acids. The EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS) provides a scientific opinion re-evaluating the safety of mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids (E 471) when used as a food additive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
